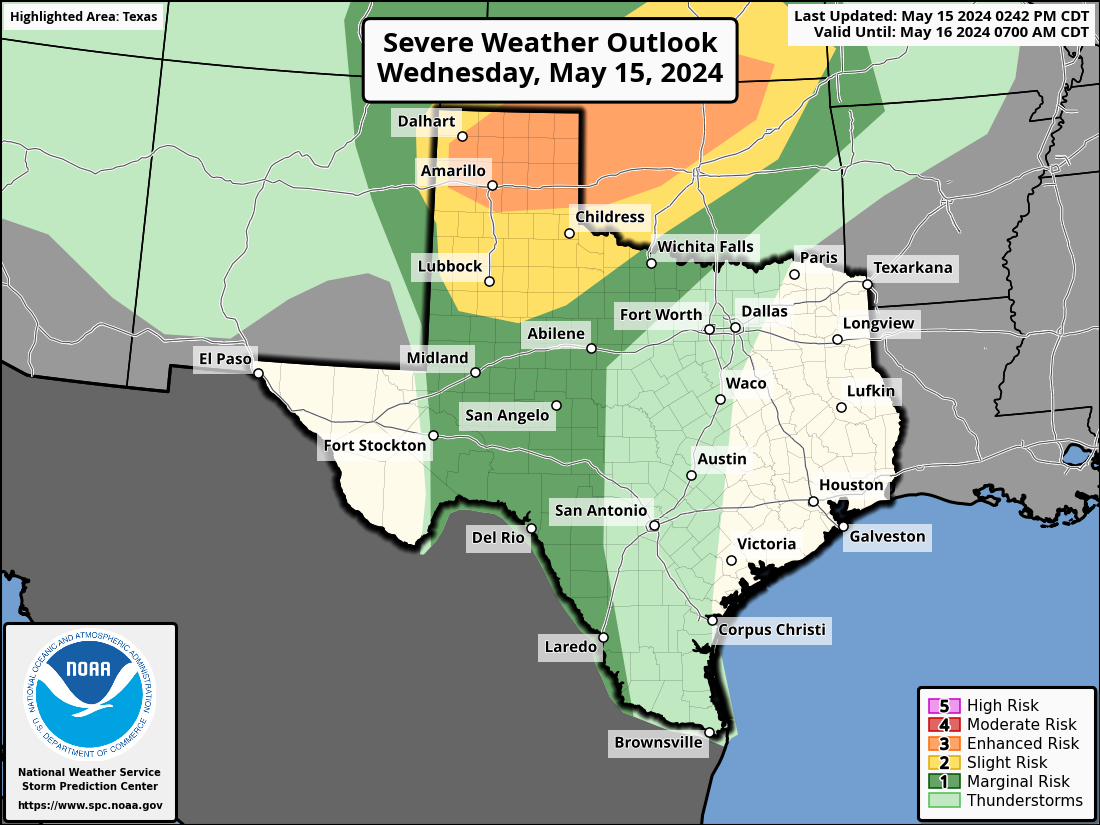
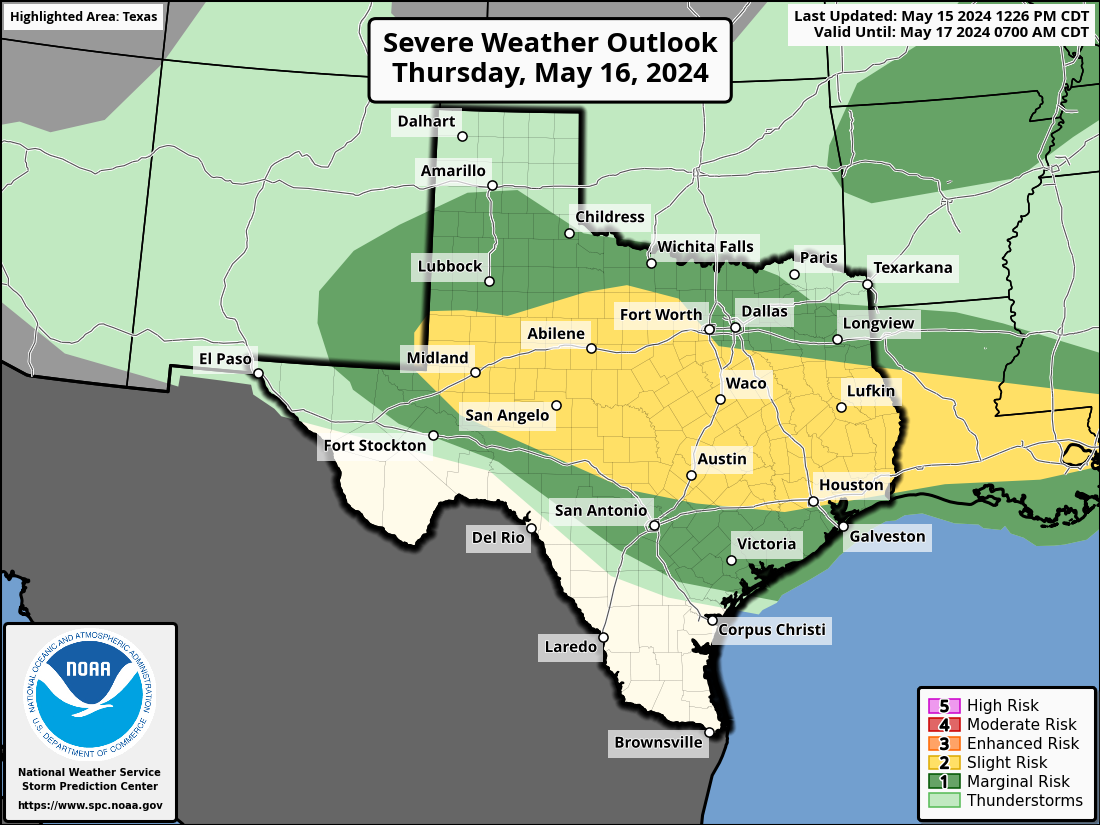
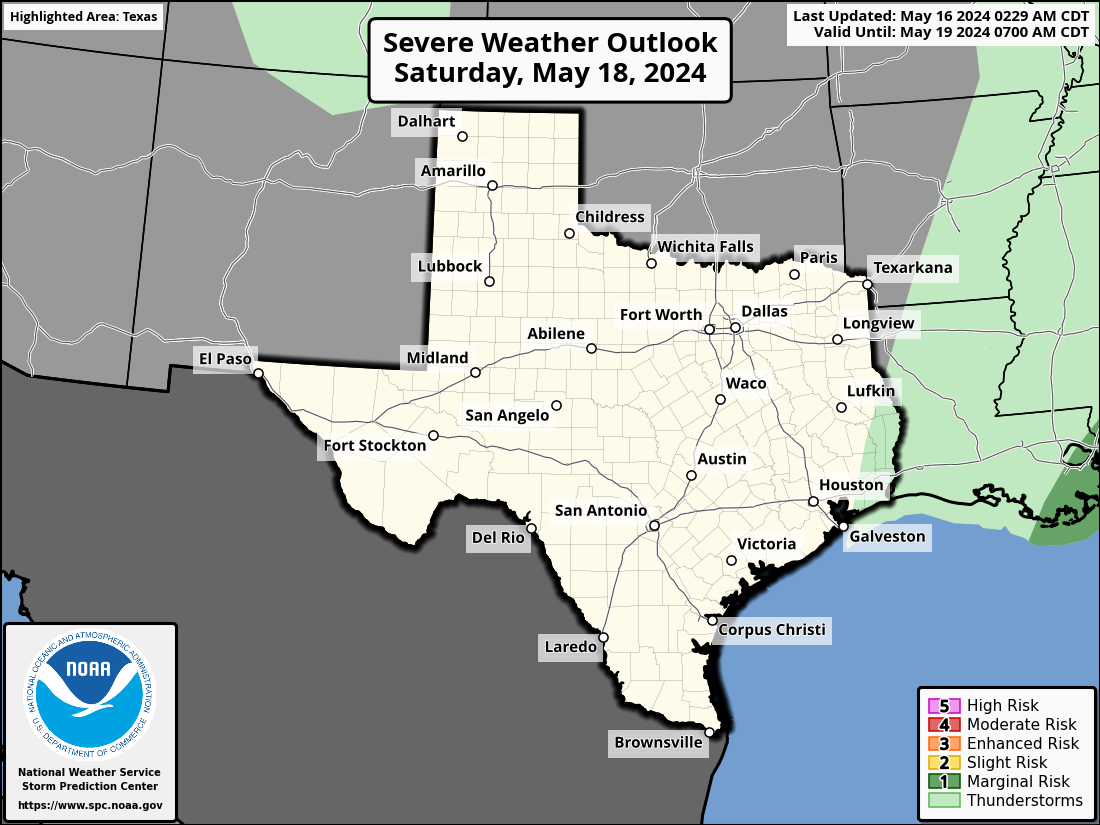
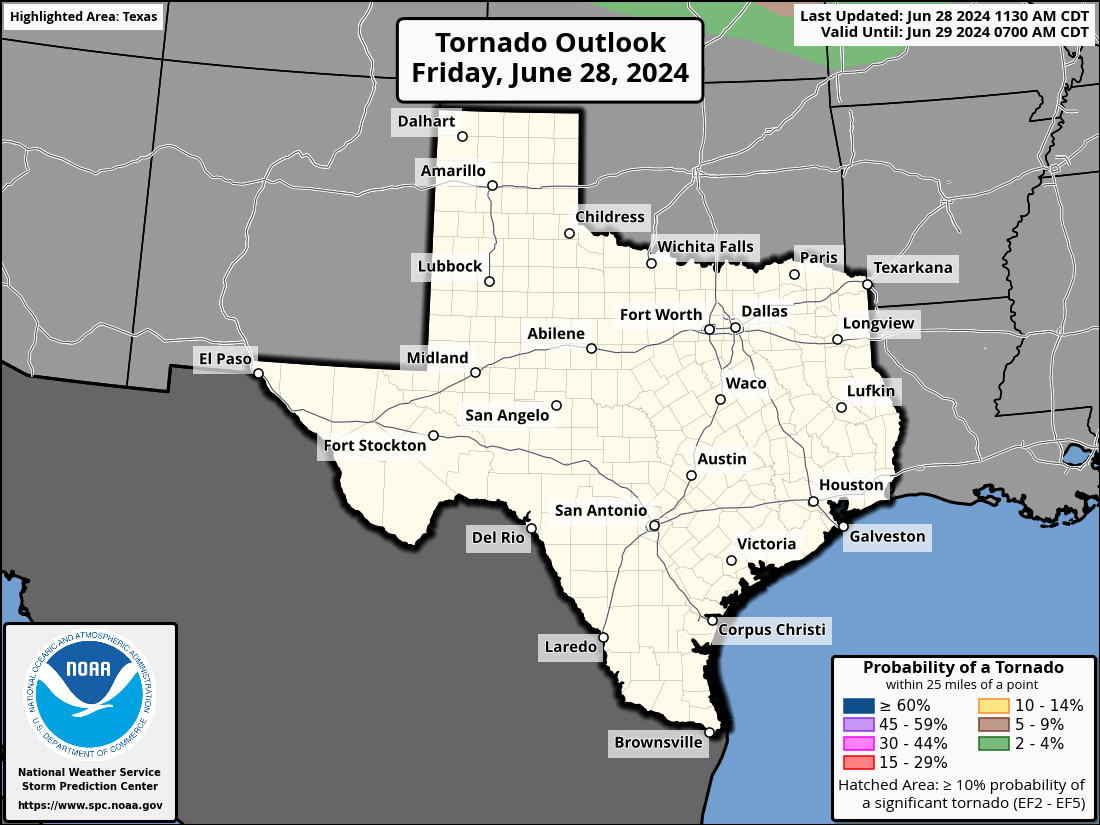
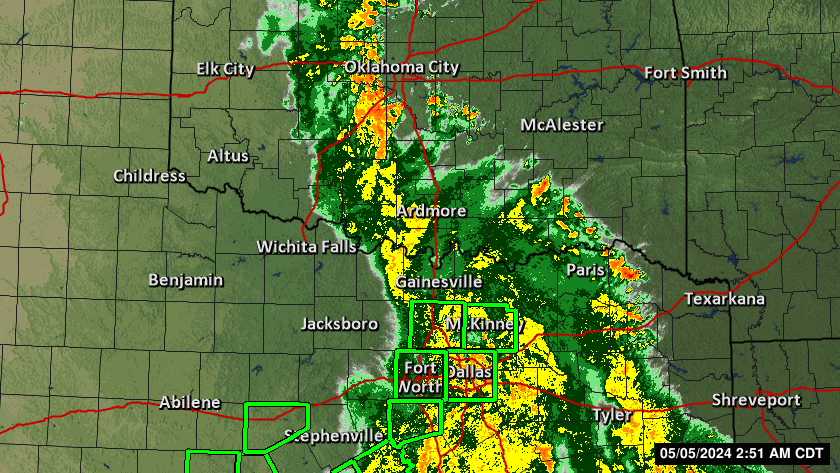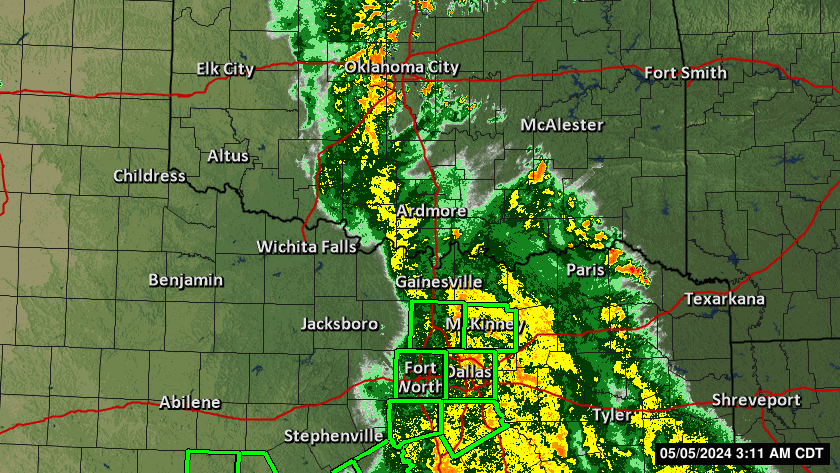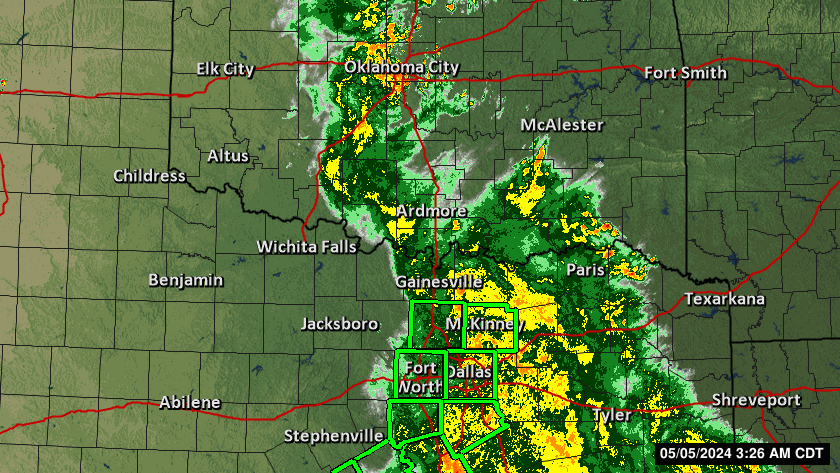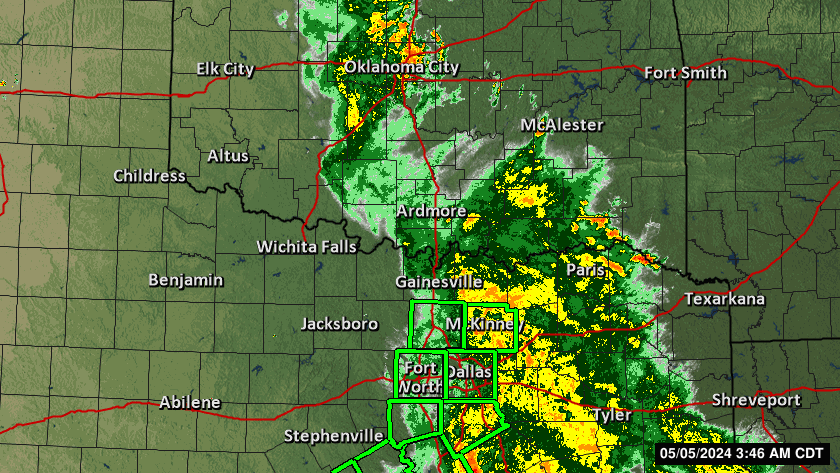
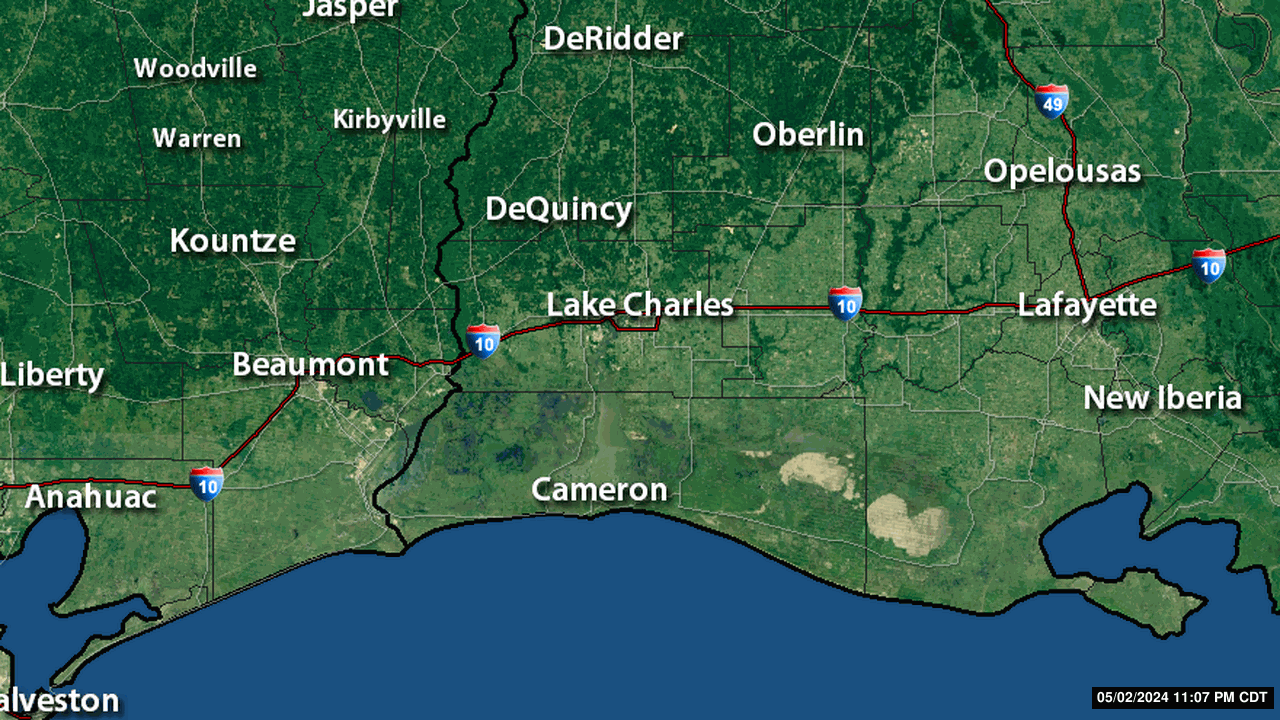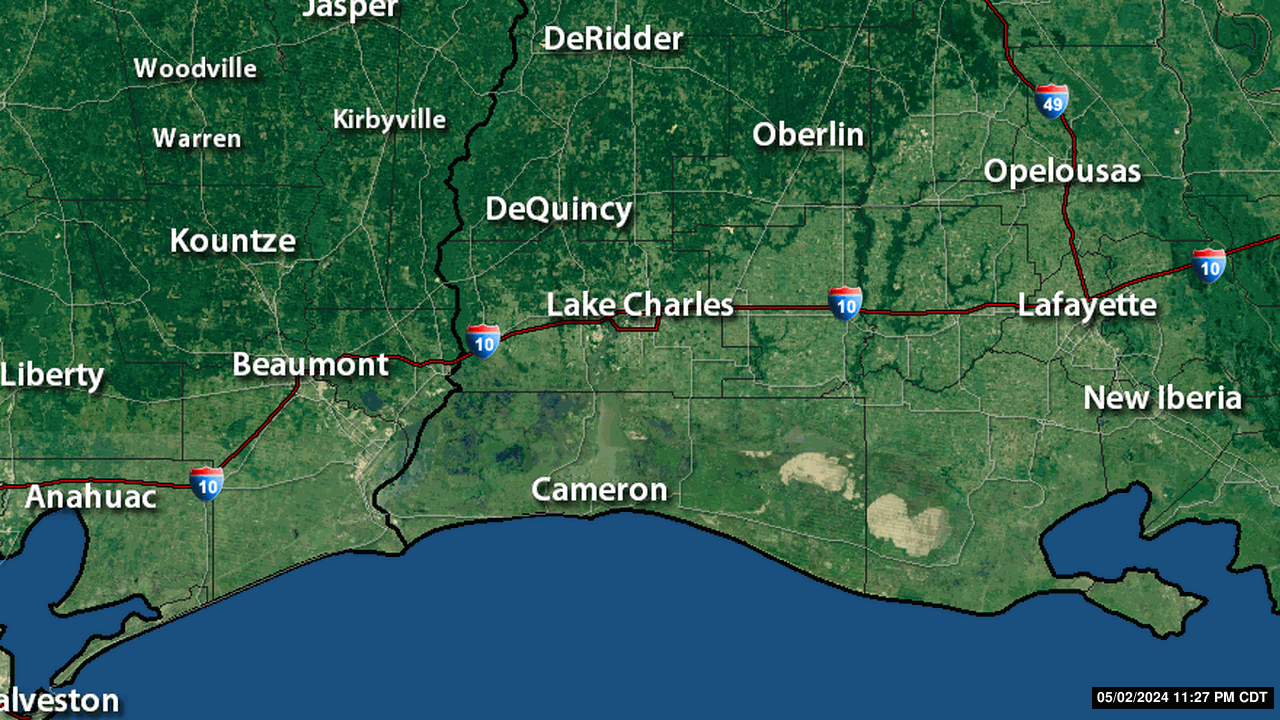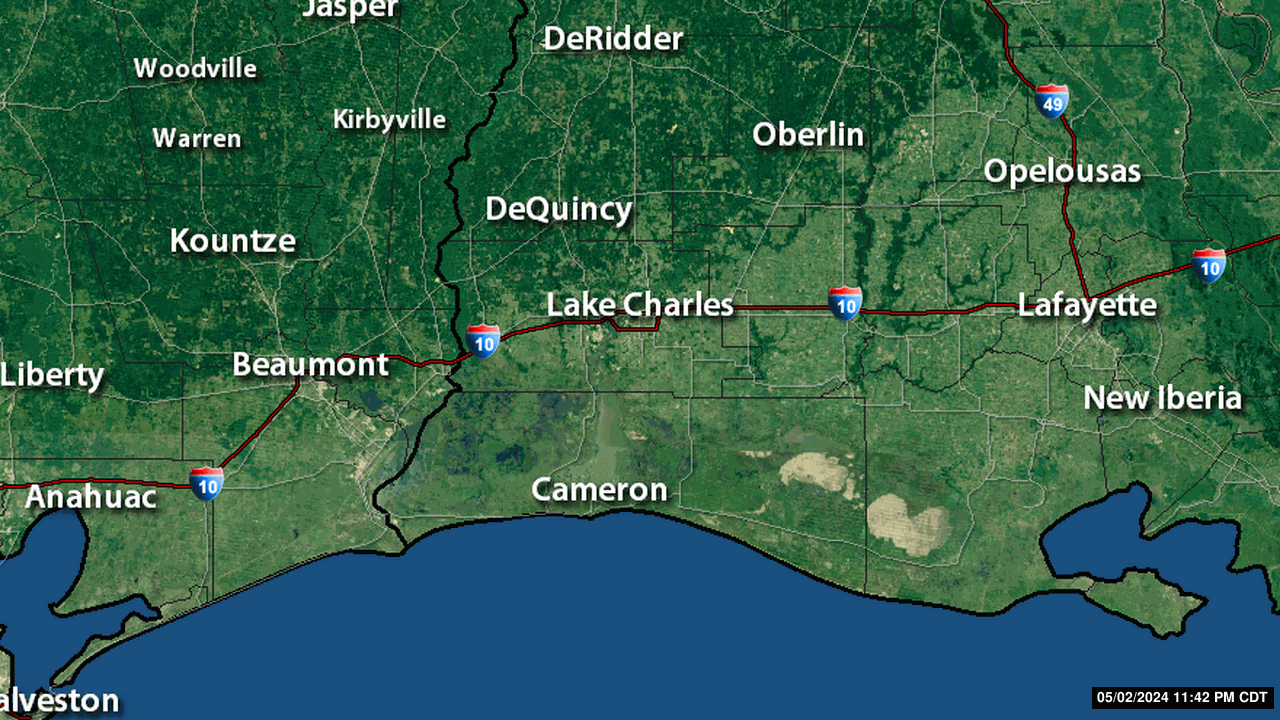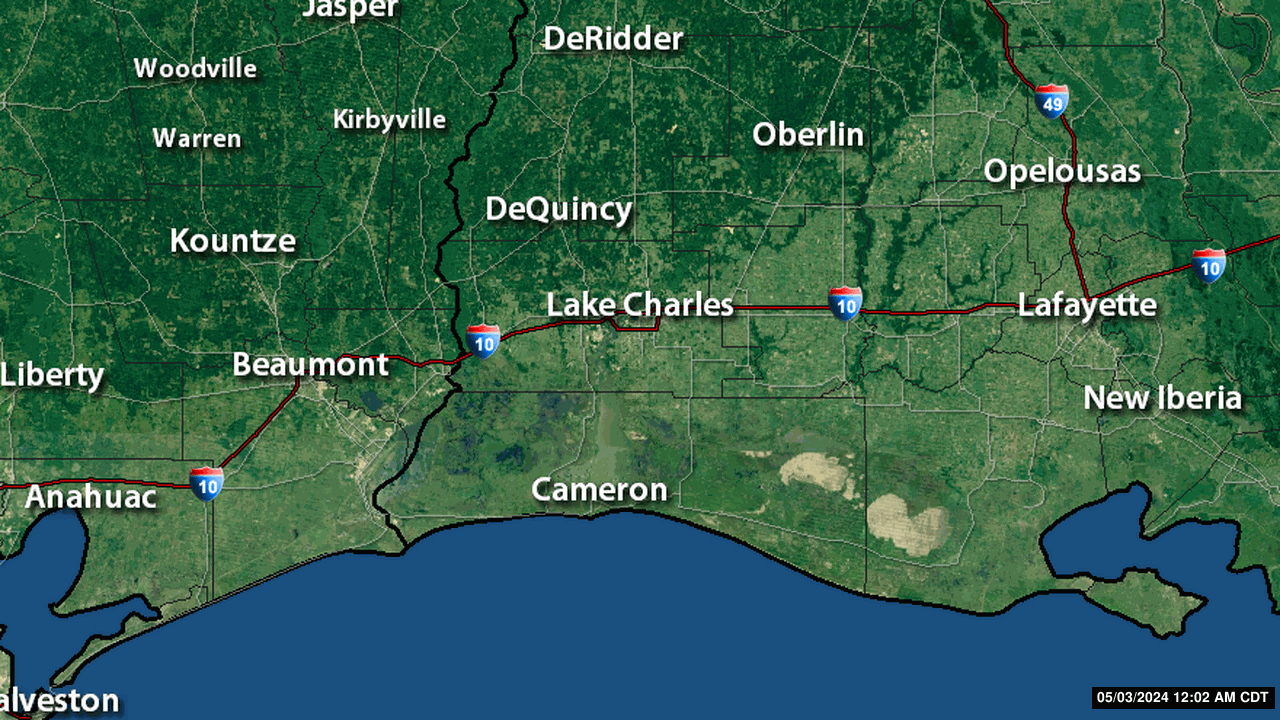
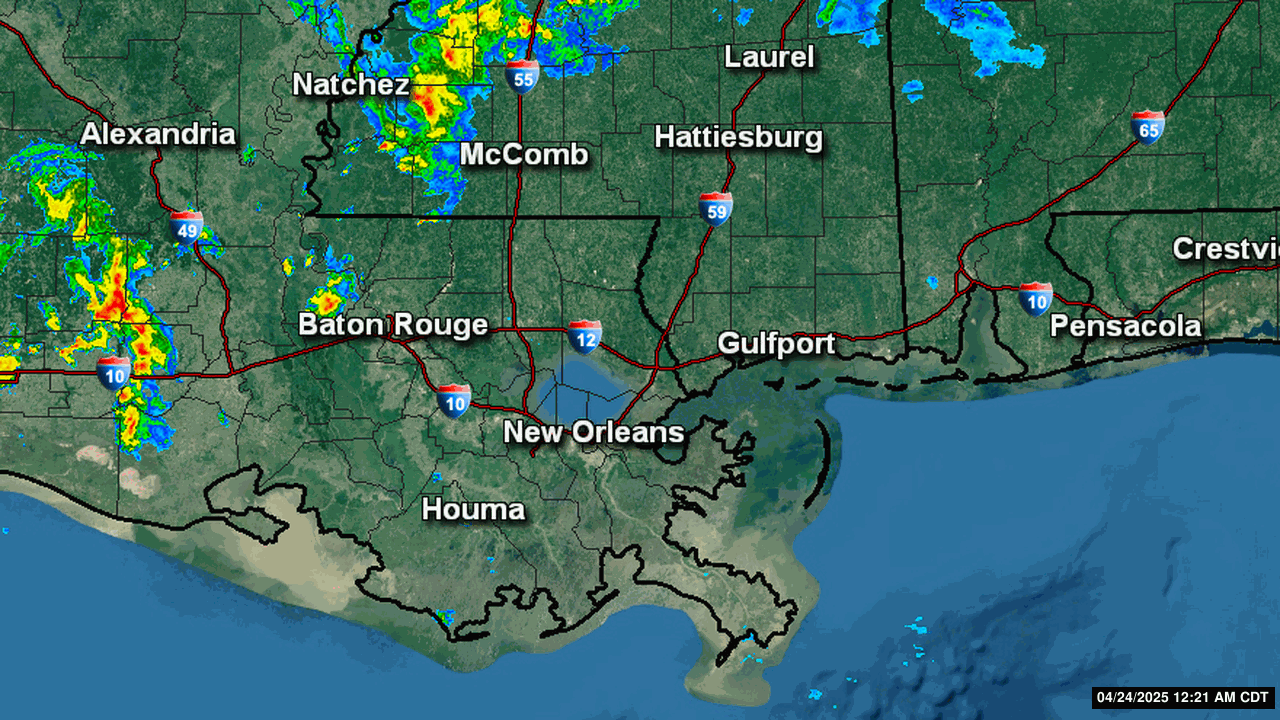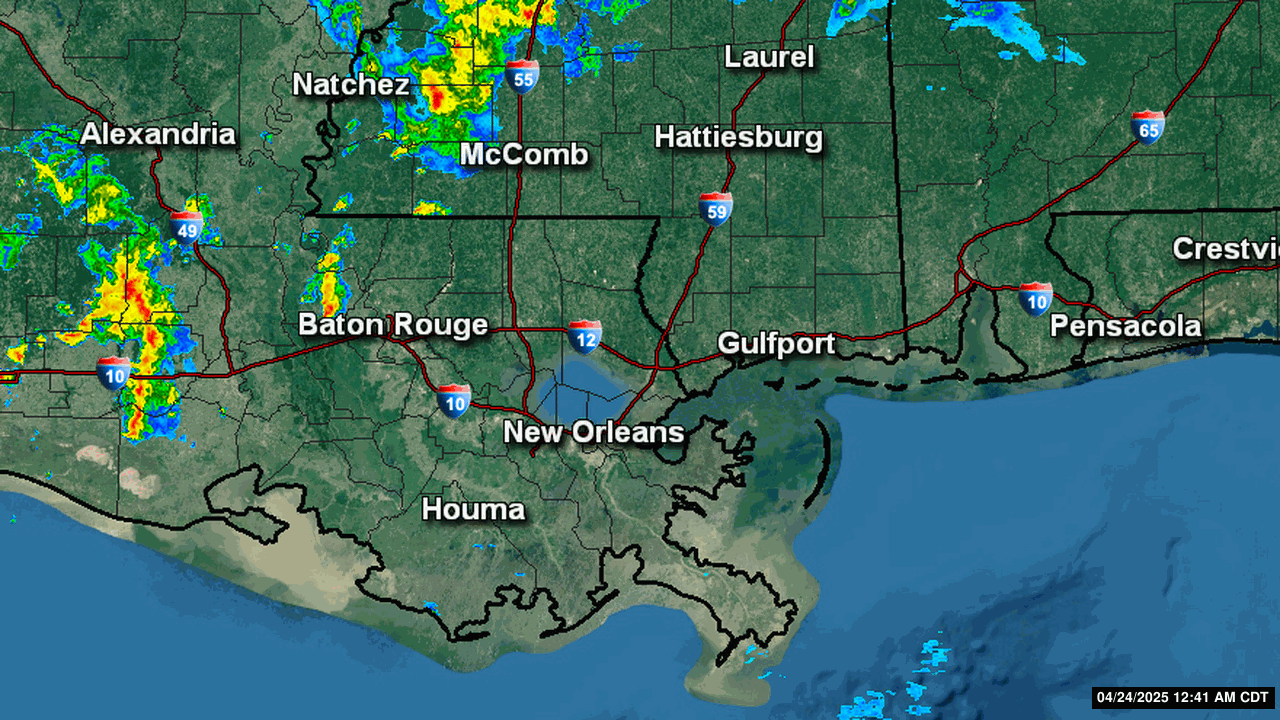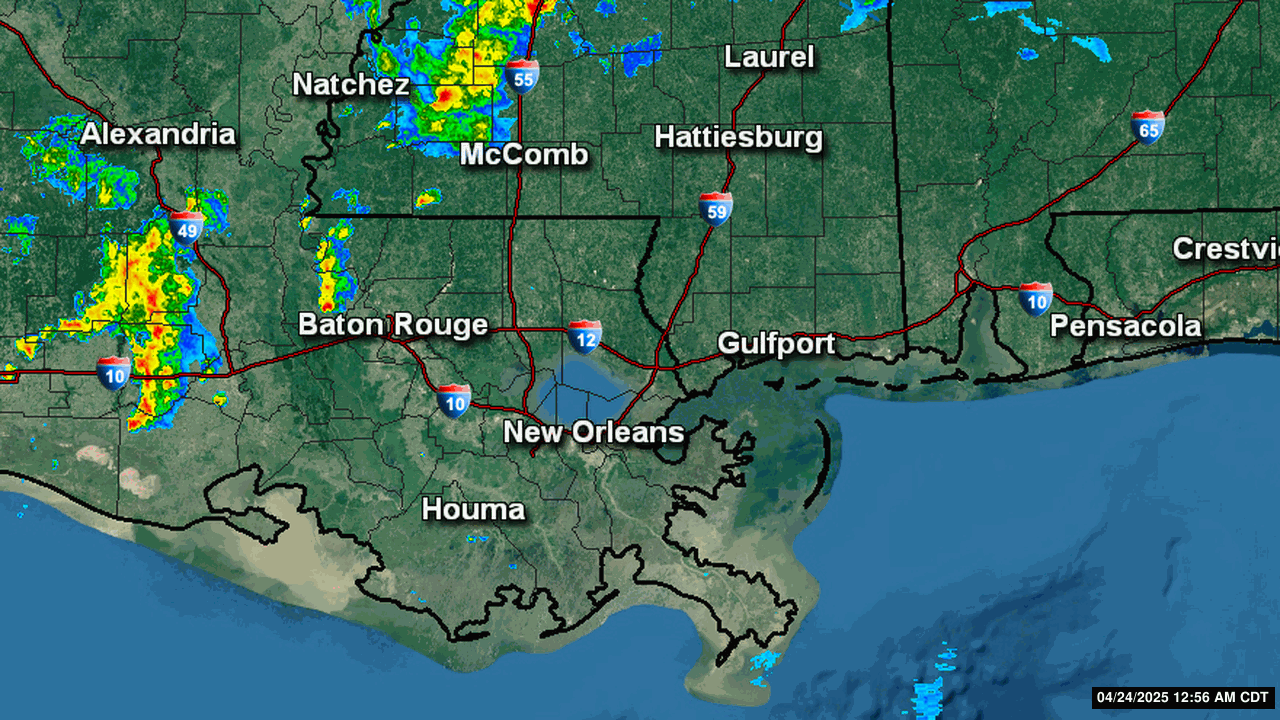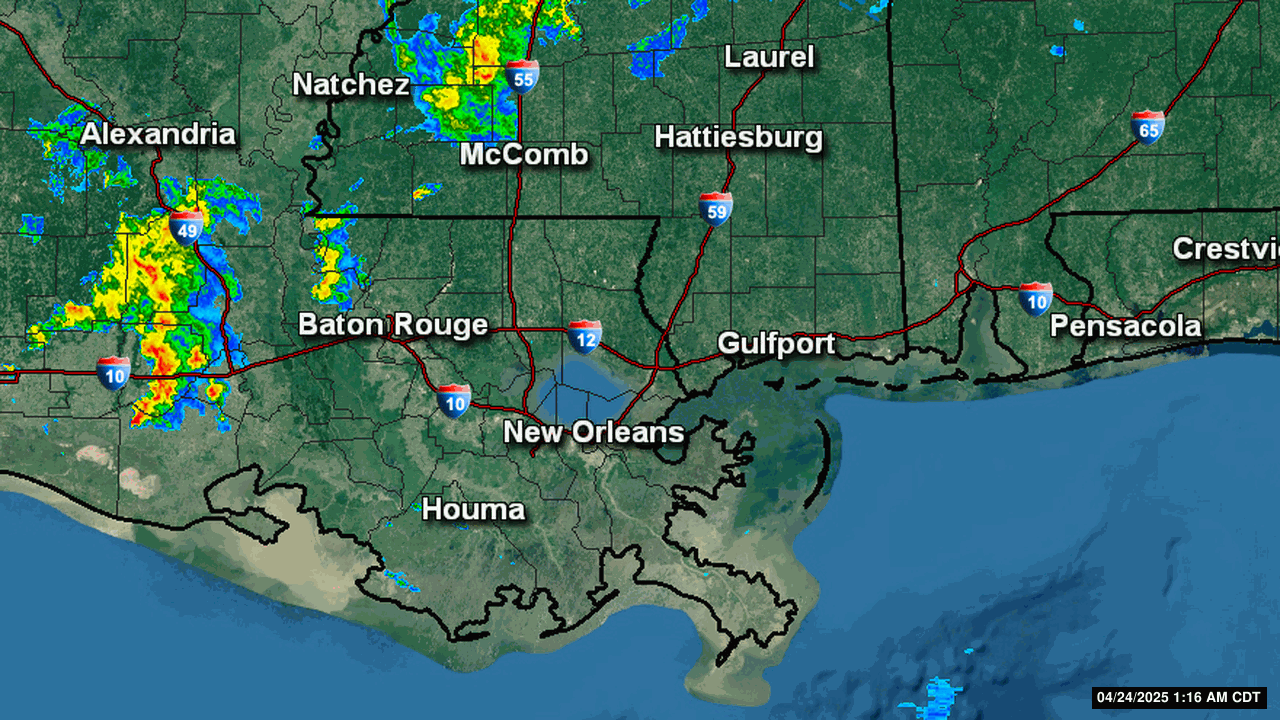
Severe Weather Indices
Bulk Richardson Number (BRN) Shear
Measures the balance between vertical wind shear and buoyancy (CAPE).
Interpretation:
BRN < 10: Strong shear, weak buoyancy; sustained storms unlikely but rotating supercells possible with forcing.
BRN 10–45: Favorable for supercell development.
BRN > 50: Weak shear, high CAPE; favors multicellular storms.

MUCAPE (Most Unstable Convective Available Potential Energy)
Indicates potential energy available for convection; higher values mean greater storm potential.
Scale: <300 low, 300–1000 weak, 1000–2000 moderate, >2000 high (strong storms likely).

Storm Relative Helicity (SRH)
Measures potential for cyclonic updraft rotation (important for tornado potential).
Thresholds:
~150: Supercell development possible
150–299: Weak tornadoes possible
300–449: Strong tornadoes possible
>450: Violent tornadoes possible

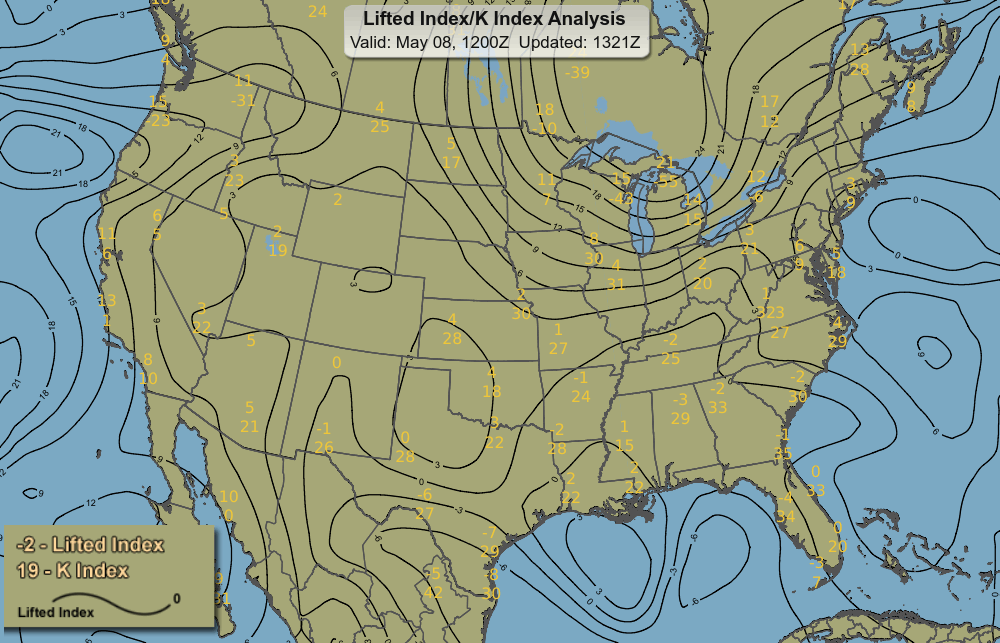
Lifted Index (LI)
Temperature difference between lifted parcel and environment at 500 hPa; negative values indicate instability.
Scale:
≥6 very stable (no storms)
1 to 6 stable (storms unlikely)
0 to -2 slightly unstable (storms possible)
-2 to -6 unstable (storms likely)
<-6 very unstable (severe storms likely)
Precipitable Water
Total water vapor in atmospheric column; higher values suggest heavy rainfall potential.
Supercell Composite Parameter
Composite index highlighting areas favorable for supercell thunderstorms.

K Index
Measures thunderstorm potential based on moisture and lapse rates.
<30 some potential; >30 better chance heavy rain storms; 40 best chance heavy rain and storms.

Total Totals Index
Combines temperature and moisture measures to assess thunderstorm potential.
40–45 thunderstorms possible; 45–50 severe storms possible; ≥55 severe storms likely, tornado possible.

Tornado Helicity Index (TEHI)
Values > 2 or 3 indicate cyclonic supercells with increased tornado potential.
Negative values favor rare anti-cyclonic supercells.

Haines Index
Indicates potential for wildfire growth based on dryness and atmospheric stability.